
For example, one study showed that compared to controls, children with perinatal asphyxia had smaller hippocampal volumes that were associated with poorer long-term visuospatial memory 46. Thus, perinatal hypoxia has been shown to account for the subsequent profile of long-term cognitive impairment in the general population 45. Perinatal hypoxia is further thought to have especially serious effects on the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, which are responsible for several neurocognitive functions including memory, language, executive function and attention. Consequently, the 1- and 5-min Apgar scores are influenced by overlapping sets of factors and are thus highly correlated 40, 44. It is important to note that those events and conditions occurring during pregnancy can lead to acute perinatal events compromising oxygen availability at birth, as well events such as hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, hypotony. In addition to delivery complications, a low Apgar score at 5 min has been suggested to reflect events or conditions prior to birth (e.g., abnormalities of gestational length and prenatal growth, congenital malformation) 40, which may have an impact on neurodevelopment 41, 42 and cognitive function 43.

Studies have suggested that a low Apgar score at 1 min often reflects acute perinatal events compromising oxygen availability at birth 38 which may influence neurodevelopmental pathways related to cognitive functioning 39. The score is typically assigned at 1 min and 5 min after delivery.
#Apgar score skin
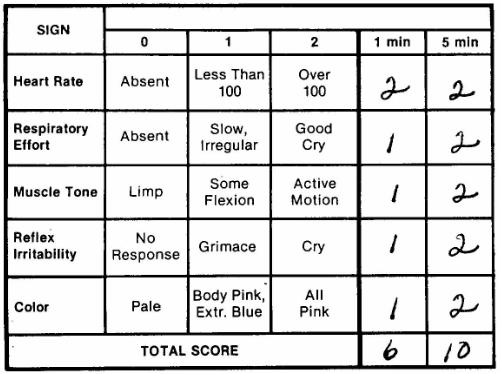
It is based on clinician observation of the newborn’s skin complexion, heart rate, reflex irritability, muscle tone, and respiratory effort, with lower scores reflective of greater problems 37. In this regard, the Apgar scoring system is an indicator of perinatal adverse events and vulnerabilities 36. Among the factors contributing to this variability, those occurring in the perinatal period (starting with the 20th or 28th week of gestation through the 1st or 4th week after birth) may be of special importance because this is a period of great vulnerability for the developing brain 24.ĭrawing on studies in the euploid population, the association between perinatal events and long-term cognition is well established 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35. In addition, certain comorbidities associated with trisomy 21 (i.e., congenital heart defects, sleep disorders, low thyroid function) are also thought to contribute to this variability 19, 20, 21, 22, 23. In this regard, previous investigations have suggested that differences in genetic 14, 15, 16 and environmental factors 17, 18 between individuals with DS are related to the degree of impairment in specific cognitive and behavioral areas. Understanding which factors contribute to the observed within-syndrome variability is crucial, and one of the main challenges to an etiology-specific approach to intervention for those with DS 13. Several other studies have shown that other cognitive areas, such as executive function, attention, and language are also quite variable across individuals with DS 5, 9, 10, 11, 12. However, it is important to note that the cognitive phenotype described above is variable across individuals with DS 7.įor example, one study reported that standard deviations for implicit memory scores were almost three times larger in a group of individuals with DS compared with a cognitive-level matched group of TD individuals indeed, some individuals with DS even outperformed TD controls 8. This profile is characterized by a general cognitive delay, relative strengths in nonverbal abilities, and impairments beyond mental age expectances in language, phonological processing, verbal memory and verbal working memory 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.

Although the DS phenotypic features are variable, when compared either to typical developing (TD) controls or to other neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs), a distinctive cognitive profile is generally observed. DS is a complex condition that affects both physical and cognitive development. Down syndrome (DS) is the most common known genetic cause of intellectual disability (ID) and results from an extra copy of all or part of chromosome 21 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
